The Evolution of Software Architecture
The journey from a creative spark to a technically sound software architecture has traditionally been a manual, fragmented process that consumes hundreds of hours. For decades, architects and business analysts have struggled with the disconnect between high-level business goals and low-level technical specifications. However, the introduction of the AI-Powered Use Case Modeling Studio in January 2026 has revolutionized this workflow. This guide explores how this all-in-one intelligent environment allows teams to transform simple goal statements into comprehensive suites of UML diagrams and professional documentation in seconds.
Overcoming the “Blank Page” Syndrome
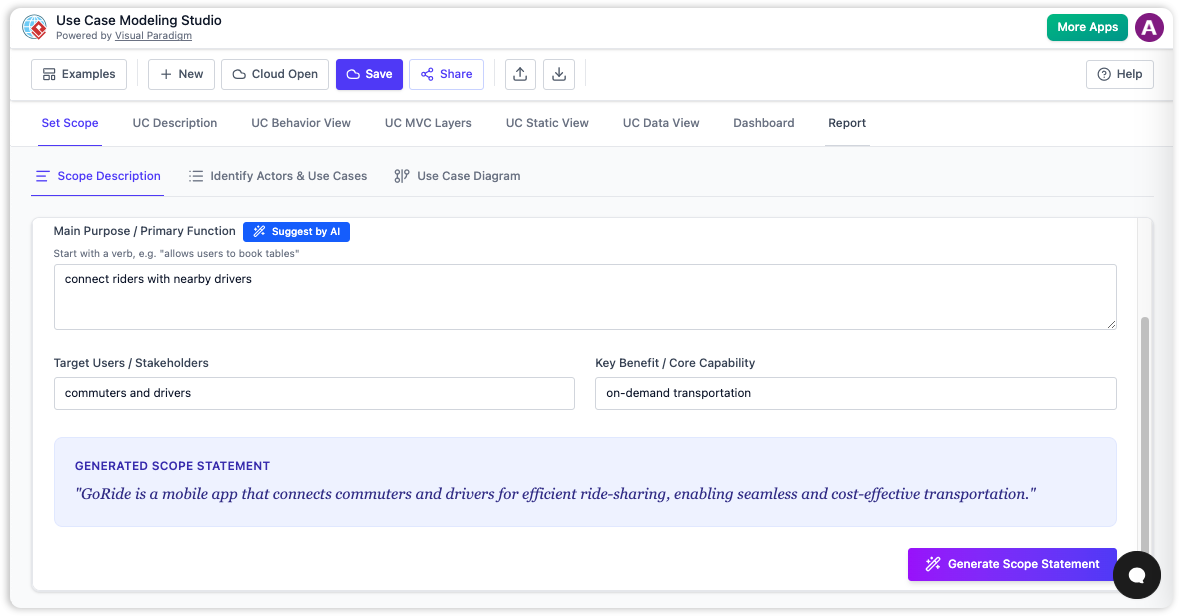
The most difficult part of system design is often the beginning. Business analysts and architects traditionally spend days painstakingly drafting initial requirements, facing the daunting “blank page” hurdle. The new AI-powered workflow eliminates this friction by focusing on intent rather than syntax.
Through a feature known as the “Set Scope” foundation, the AI utilizes a “Suggest by AI” engine. This allows users to input a high-level system goal—such as “Design an online booking system”—and instantly receive a structured Scope Statement. This statement serves a critical technical purpose: it acts as the “single source of truth.” By detailing the core purpose, target users, and key benefits immediately, the system ensures that all downstream generations—from diagrams to code structures—are directly tied to business needs.
Automating Requirements Engineering
Once the scope is established, the transition from vague concepts to structured requirements happens automatically. The AI analyzes the scope text to identify the necessary interactions, effectively acting as an automated requirements engineer.
Identifying Actors and Entities
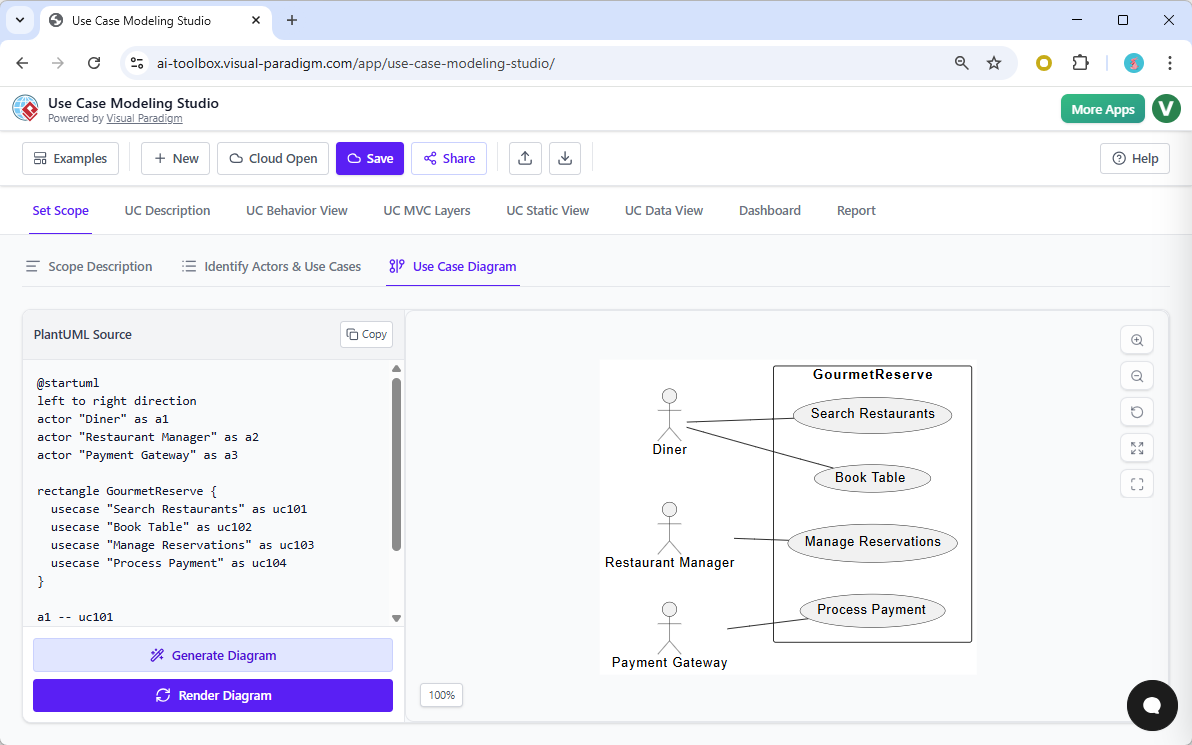
The system parses natural language to suggest Actors. These are the entities interacting with the system, ranging from human users like “Diners” or “Managers” to external systems like “Payment Gateways.”
Defining Use Cases
Simultaneously, the AI generates Candidate Use Cases. These represent the essential functions required to fulfill the scope, such as “Book Table,” “View Menu,” or “Manage Reservations.” This stage moves the project from a conceptual phase to a structured list of requirements without requiring the architect to manually list every possible interaction.
Instant Generation of Multi-Perspective Blueprints
The true power of the studio lies in its ability to handle both logic and layout simultaneously. In traditional workflows, translating text into visual models is a labor-intensive task using drag-and-drop tools. The AI-Powered Use Case Modeling Studio transforms textual flows into a complete suite of visual models with a single click.
The system generates three distinct categories of diagrams to provide a 360-degree view of the architecture:
- Use Case Diagrams: High-level overviews visualizing actors as stick figures and use cases as ovals within a system boundary.
- Dynamic Behavioral Models: Detailed Activity Diagrams that map workflows and Sequence Diagrams that illustrate how objects and actors interact over time.
- Structural Models: Technical blueprints including Class Diagrams (identifying entities, attributes, and operations) and Entity-Relationship Diagrams (ERDs) for database schema design.
Refining for Technical Accuracy and MVC Mapping
Generating a diagram is only useful if it is technically sound. The AI applies strict rules of software design to ensure the plan is implementable. Using the “Refine with AI” feature, the studio can automatically detect and inject complex UML relationships, such as <<include>> and <<extend>>, ensuring the models adhere to industry standards.
Furthermore, the tool bridges the gap between requirements and implementation by mapping use cases to Model-View-Controller (MVC) layers. This feature identifies:
- Model: The data structures required.
- View: The UI screens needed for interaction.
- Controller: The logic governing the data flow.
This mapping provides developers with a clear roadmap, reducing the ambiguity that often leads to technical debt.
From Modeling to Professional Reporting
The final step in transforming an idea into architecture is formalizing it for stakeholders. The studio features One-Click SDD Reporting, which aggregates the scope, use case specifications, visual models, and AI-generated test plans into a polished Software Design Document.
These reports address the needs of diverse audiences and can be exported immediately as professional PDFs for executive review or git-friendly Markdown files for developer repositories.
Comparison: Traditional vs. AI-Powered Design
| Feature | Traditional Workflow | AI-Powered Studio |
|---|---|---|
| Starting Point | Manual drafting of requirements | “Set Scope” via simple prompts |
| Modeling | Drag-and-drop diagramming | Instant multi-perspective generation |
| Technical Detail | Manual mapping of MVC/Databases | Automated MVC and ERD generation |
| Documentation | Hours of compiling Word docs | One-Click SDD Export |
The Role of the AI as a Bilingual Mediator
To understand the impact of this technology, one should view the AI-Powered Use Case Modeling Studio as a bilingual project mediator. In software development, business stakeholders often speak the “language of goals,” while developers speak the “language of blueprints.”
The AI acts as a real-time translator that goes beyond simple text translation. It simultaneously draws the maps, floor plans, and instruction manuals needed to ensure both parties are building the exact same house. by automating the translation of ideas into structured architecture, teams can focus on innovation rather than documentation.