As Enterprise Architecture grows in scope and complexity, ArchiMate diagrams often expand into dense networks of elements and relationships. While these models are powerful, editing them has traditionally been slow and error-prone. Even small changes can require navigating multiple views, updating relationships, and adjusting layouts manually.
Conversational modeling offers a new approach. Instead of interacting with diagrams directly, architects interact with an AI through text prompts. The AI interprets intent, applies ArchiMate rules, and updates the model automatically. This changes how architects work with complexity and shifts modeling from a visual task to a conceptual one.
What Is Conversational Modeling in ArchiMate?
Conversational modeling is the ability to create and modify architecture models through natural language interaction. Rather than dragging shapes or manually editing connections, the architect describes what needs to change.
In an AI-enabled ArchiMate tool, a prompt such as “Replace the legacy billing system with a cloud-based service and update all dependent processes” is enough to trigger coordinated changes across multiple layers.
The model remains structured and standards-compliant, but the interaction becomes simpler and more intuitive.
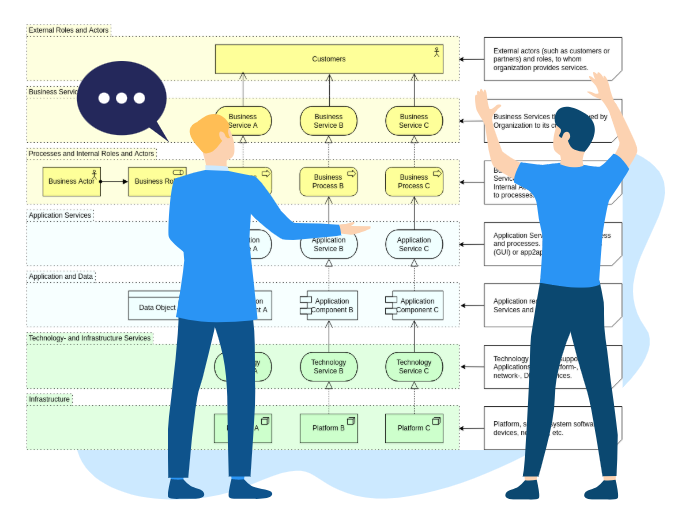
Why Editing Complex ArchiMate Diagrams Is Traditionally Difficult
Complex ArchiMate diagrams often span multiple viewpoints, layers, and abstraction levels. A single architectural change may affect:
- Business processes
- Application services
- Data objects
- Technology infrastructure
- Motivation and strategy elements
Manually managing these updates introduces several problems. Architects must remember where elements appear, ensure relationships remain valid, and maintain consistency across views. Over time, this effort discourages frequent updates and weakens trust in the model.
Conversational modeling directly addresses this friction by treating complexity as something the tool manages, not the architect.
How Text Prompts Translate into Model Changes
When an architect enters a text prompt, the AI diagram generator analyzes both the request and the existing model context. It identifies relevant elements, relationships, and viewpoints before applying changes.
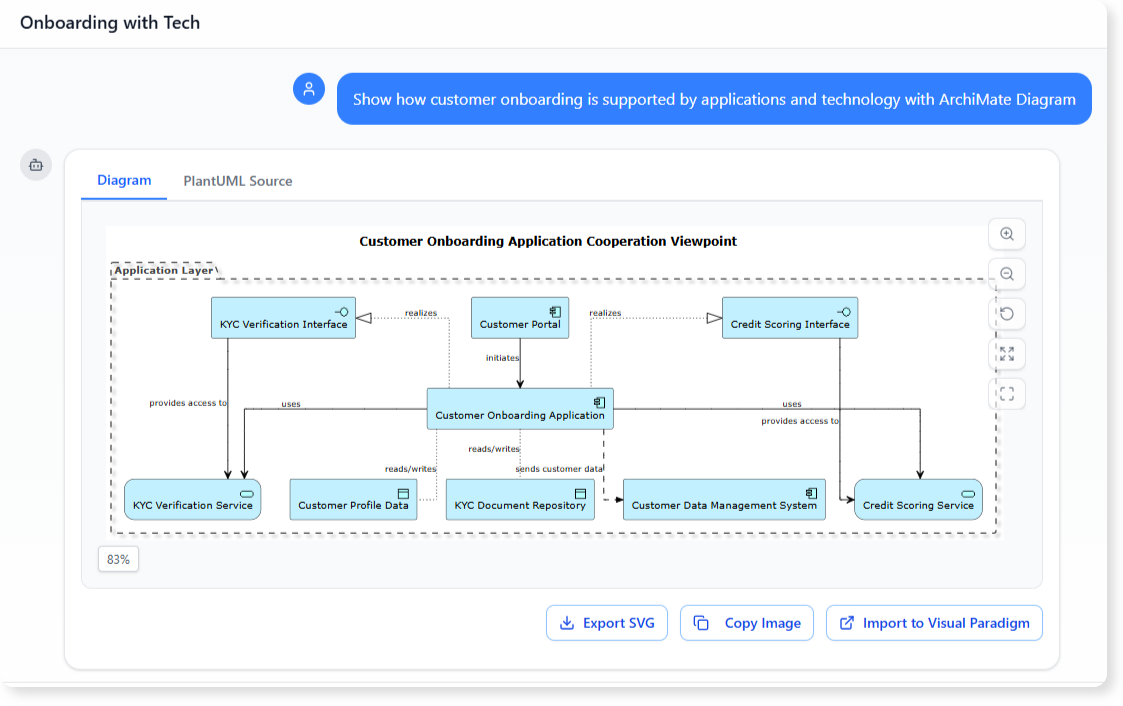
For example, a prompt like “Show how customer onboarding is supported by applications and technology” can result in:
- Selection of the relevant business process
- Identification of supporting application services
- Inclusion of underlying infrastructure
- Generation of a focused ArchiMate viewpoint
The architect does not need to specify every modeling detail. The AI applies modeling logic based on ArchiMate semantics and best practices.
Maintaining Architectural Integrity with AI Assistance
A common concern is whether conversational modeling compromises modeling discipline. In practice, the opposite is true.
AI-assisted ArchiMate tools enforce valid relationships, layer boundaries, and element usage automatically. This reduces accidental misuse of notation and improves overall model quality. Instead of remembering syntax rules, architects focus on intent and meaning. The tool ensures that the resulting model remains compliant with ArchiMate standards.
Improving Collaboration Across Roles
Text-based interaction lowers the barrier to participation. Stakeholders who are unfamiliar with ArchiMate notation can still interact with the model by asking questions or requesting views. This makes Enterprise Architecture more collaborative. Business leaders, analysts, and IT teams can engage with the architecture without learning diagramming techniques. The AI acts as an interpreter between intent and formal structure.
The Architect’s Role in a Conversational Modeling World
Conversational modeling does not eliminate the architect’s role. It elevates it. Architects remain responsible for defining scope, validating assumptions, and interpreting results. The AI handles execution, not judgment. By removing the need to manage visual complexity manually, conversational modeling allows architects to focus on design quality, alignment, and long-term impact.
Conclusion
Conversational modeling transforms how complex ArchiMate diagrams are created and maintained. By using simple text prompts, architects can edit large-scale models quickly, accurately, and consistently. This approach reduces overhead, improves collaboration, and keeps architecture aligned with real-world change.
As AI-enabled ArchiMate tools continue to evolve, conversational modeling will become less of a novelty and more of a standard way to work with Enterprise Architecture.